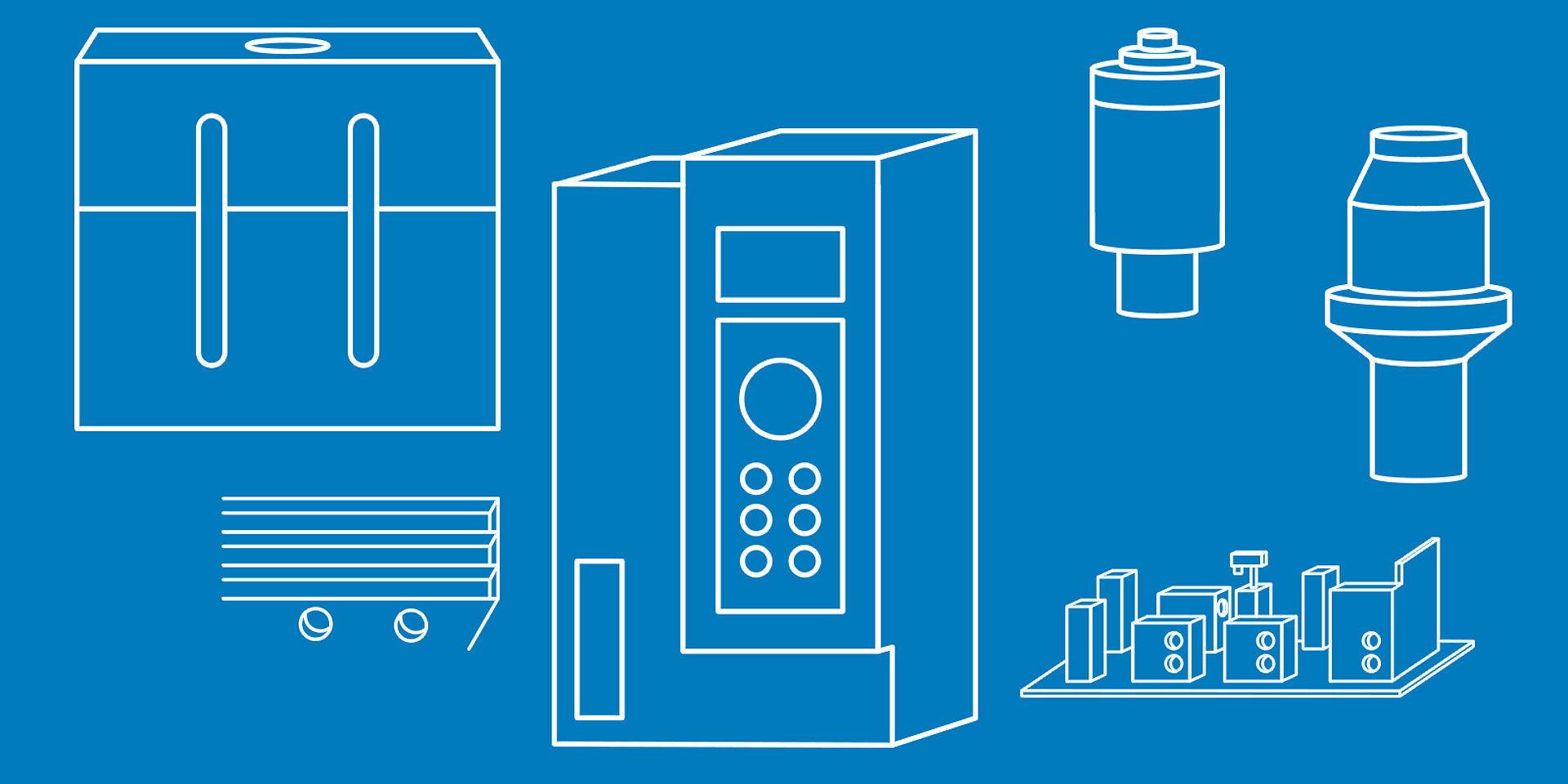
Welding using ultrasonics
When you hear the term ultrasonics, you probably don't think about welding right away, you probably think about medical ultrasonic devices. In fact, ultrasonics can also be used to weld various materials such as plastics, nonwovens, metals or packaging. This works by converting high voltage from a generator into mechanical vibrations (ultrasonics). Sonotrodes then introduce these into the components being welded. The vibrations create friction heat and the materials start to melt. By applying additional pressure, the components can then be joined.
Advantages
Ultrasonic welding offers a number of advantages over conventional joining methods such as adhesive bonding or inert gas welding:
- Ultra fast: The materials are melted and joined in split seconds.
- Consistently high quality: Precise control technology ensures reproducible, precise and appealing results.
- Flexible: Can be adapted to suit the most varied of materials, shapes and processes.
- Environmentally friendly: Ultrasonic welding is clean, energy-efficient and doesn't produce any waste products.
- Cost efficient: Short process cycles, low energy consumption, no additional tools or aids such as screws, adhesives etc.
Ultrasonic welding
To put it simply, sound is vibration that you can sometimes hear. Ultrasonics are different: These are noiseless sound waves. They are often used in industry. Ultrasonic welding is suitable for various materials such as plastics, metals or nonwovens. The right weld tool and the setting of the process parameters are vital for a good weld result. This is the only way that a consistently high quality is guaranteed.
Success stories from our customers
Together with our customers, we solve over 1,500 applications worldwide every year. Read our customer stories to find out how our ultrasonics solutions help them produce more safely, efficiently and sustainably.